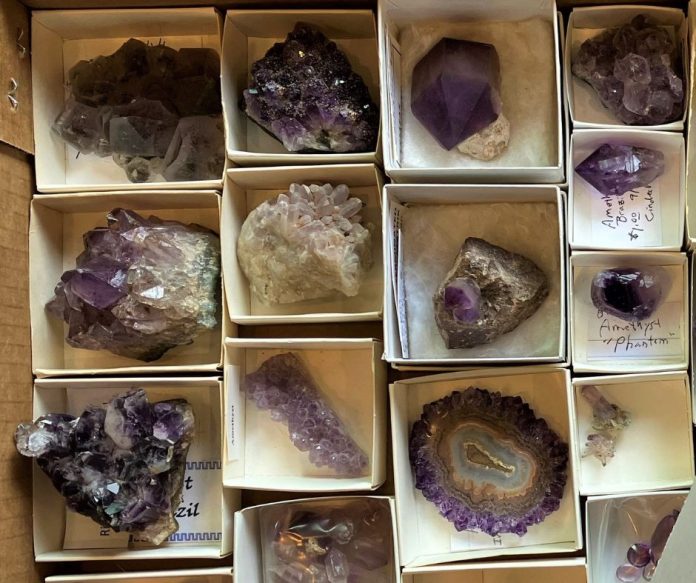
How to store a rock collection properly is a question asked by many rock collectors. Many amateurs have amassed minerals, fossils, or hand-crafted jewelry that, collectively, add up to a small fortune. All too often, such collections get broken up and sold for pennies on the dollar after the death of the collector. Worst case, they end up in a landfill because kids can’t be bothered with “Dad’s old rocks.” What’s your rock collection worth? How can you insure it against theft or damage? What plans should you make for heirs or to otherwise transition? Most of us are at a loss when it comes to such questions. Where to even begin?

How to Store a Rock Collection for Documentation
Know what you’ve got and document it! If self-collected, record the locality and date of collection. If purchased, record when, where, from whom, and the price paid. If trading with a fellow collector, record the transaction. “Provenance” is important in the collecting world and adds value. Keep a ledger and include a catalog number on each specimen. On a personal note, as a member of a gem club, I receive collections for our club museum and it is a rare joy when donations come with numbered specimens and a catalog. You can build a catalog with a handwritten ledger or, better, with database software. Whatever route you choose, don’t just keep loose cards with specimens. I knew a lady who lived in a rambling Victorian house and kept a Victorian-style collection—a bit of everything haphazardly placed in an eclectically cluttered funhouse. Regrettably, she stored all the info on loose cards and in her head. Over the years, maids vacuumed up the cards while her memory of the specimens disappeared. This left her heirs with a superb collection much diminished in value. If you have specimens you purchased, keep the cards that came with them but also maintain an updated rock collection catalog.
|
Key Takeaways in Documenting a Rock Collection • Don’t just know what you’ve got. Document it! • The more detail, the better. • The best catalog is electronic, accompanied by photos. • Update annually to decommission and/or add specimens. • Keep a copy of your catalog in a safety deposit box. |
Assessing Your Collection
After documenting your collection, consider having it appraised. Most collections are “specimen collections” of primarily common pieces. While a fossil may be near and dear, if it’s not truly world-class, it’s not worth your time to appraise. Pare down and focus on stuff that is truly rare, unusual, or would be in demand in a market environment. Per the late-great comedian George Carlin, junk is stuff we toss, but stuff is junk we keep. Assess good stuff, not junk!
Where to Get an Appraisal
Where to get a rock collection appraisal? Many gem clubs get requests but are not qualified and as nonprofits are not allowed to provide legal appraisals. Fancy auction houses like Sotheby’s mean paying fancy fees. A good place to start is a local jewelry store with staff who are GIA (Gemological Institute of America) certified. While it’s easy to find someone to appraise jewelry or cut gemstones, it’s more difficult with specimen minerals or fossils. Gem show dealers might appraise what you’ve self-collected or purchased.
However, some warn against going to dealers because they may have an interest in purchasing your collection and provide a low-ball assessment then pressure you to sell to them. It’s best to go to a neutral third party. If turning to an outside entity, seek agencies with qualifications and those versed in the category best matching your collection. Such companies sometimes advertise in hobby magazines or on websites.
Although some auction houses sponsor “appraisal days” with free verbal assessments, most appraisals come with fees based on the assessed value. Appraisers may charge a “per-piece” fee, an hourly fee, or another rate for services. If turning to an appraiser with an especially large collection, negotiate regarding fees and what sort of documentation will be produced.
|
Who Are the Best Appraisers? In seeking an appraiser, look for individuals/companies associated with key organizations: • Appraisers Association of America • American Society of Appraisers • International Society of Appraisers • American Gemological Society |
Appraisal Alternative
Alternatively, do a self-assessment. If a specimen was purchased, what did you pay for it? Keep in mind: what you paid doesn’t necessarily reflect worth. One person paid $9,000 for a sapphire only to discover it was worth $30 after a professional appraisal. That said, compare specimens in your collection against going rates via online shops like Amazon, eBay, and Etsy. Search the internet and gem show aisles to see retail for “like” items.
The main thing to seek? A fair-market value you can document. Don’t go to a “We Buy Gold!” shop offering a commodity price for your carefully crafted collection of gold nuggets. What is the price fellow collectors might pay? Whatever route you choose, have a rationale behind assigned values. Use hard market data either deduced by yourself or obtained from an impartial third party, not based on sentimental value. Also, some insurance companies don’t accept self-assessments and insist on independent evaluations. This could cost you big bucks, so focus on unique pieces within your collection. Search the web for appraisers within your region.
Where to Get Insurance

After appraising a rock collection, most turn to their regular homeowner’s insurance. This can be the most inexpensive option, but while many companies are versed in insuring jewelry, not all have expertise regarding specimen minerals and fossils. And while homeowner’s insurance may provide coverage in a “personal articles floater,” such a floater may be exorbitantly expensive and most fail to offer full replacement cost. Seek better deals with specialized insurers offering “collectibles insurance.” As an example, one collector spends $120/year with a specialized insurer for a 200-piece collection worth $17,000 when her regular homeowner’s policy turned her down.
What Insurance to Get for Your Collection
You can get a rider on your homeowner’s insurance policy, but they say not to bother for individual pieces or an entire rock collection that isn’t worth at least a minimum amount. Most policies exclude or severely limit the value of coverage for collectibles, but if you have a small collection of ordinary specimens, this may be your best bet.
Alternatively, some companies focus specifically on gems and collectibles both for appraisal services and insurance for especially high-value collections. When seeking insurers—as in seeking appraisers— check advertisements within hobby magazines and/or do an internet search.
Whatever route, seek a policy insuring against theft, accidental breakage, fire/ water damage, and natural disasters. If you attend gem shows as an exhibitor, consider coverage for travel and show attendance. Finally, seek insurers versed in the unique properties involved in one-of-a-kind collectibles, including such concepts as “replacement value” versus “fair market value” or “agreed-value coverage” versus “actual or standard cash value.”
Protecting Your Rock Collection
If you wish to insure a collection, you’ll need to provide evidence that you’re protecting that collection. Store specimens in cabinets or flats. High-value items should be locked in a safe. Place small items with outsized values in a safety deposit box. Alternatively, adopt a high-strung Doberman Pinscher! As some members of my Ventura Gem & Mineral Society learned during the devastating 2017 Thomas Fire in California, even rocks burn. Have smoke detectors in every room of your home and keep them charged with fresh batteries to protect both your rocks and yourself.
Those with more means might install a sprinkler system. This is a step above, but it’s worth it when you consider what happened to the national museum in Brazil, which lacked smoke detectors and sprinkler systems and suffered a total loss of national treasure. Some choose to keep a secure location within their homes for especially valuable pieces, which can go as far as a “safe room” with a locked door and inside closets and vaults. Do your best to protect the best of what you’ve got!

Transitioning Your Rock Collection
If you’ve devoted time to documenting, appraising, and insuring your collection, you certainly want to consider what happens after you‘ve departed the scene. Do you care if your collection is broken up, or do you hope it might be kept whole? The latter is problematic unless you have an heir who shares your passion or unless you provide an endowment to a museum to pay for storage, display, and upkeep. First, consider immediate heirs. Desires should be spelled out in a will or, better, a trust. But if heirs have no interest, consider liquidating the collection in your lifespan.
If you do wish to keep it intact, build contacts with a local museum and make your wishes known. Museums want collections with clear provenance and no issues (e.g., no specimens collected from national parks or countries with human rights abuses in gemstone districts). Most cannot guarantee specimens will be put on display and can’t guarantee they won’t be decommissioned and disposed of. If you truly want your collection to have a permanent place in a museum, you may need to accompany it with a healthy cash endowment.
Continuing the Conversation…
This topic is not typically discussed within gem societies but, in my humble opinion, how to store a rock collection properly should be discussed. Our collections are a reflection of ourselves. How might we best preserve the best of ourselves for future generations?
This story about how to store a rock collection properly previously appeared in Rock & Gem magazine. Click here to subscribe. Story and photos by Jim Brace-Thompson.