Types of gemstones like sapphires and tiger’s eye are well-known and zircon has been around for two millennia, however, it’s more difficult to find stones such as vesuvianite with its origin in Mount Vesuvius. Here we’ll explore gemstones that start with the letters S to Z. Even for gemstones that are not as popular, learning the details of their origination and modern uses inspires us to look closer at them. This is the third in a three-part series covering types of gemstones by letter starting with the letters A to I and gemstones that begin with the letters J to R.
Sapphire

One of the official state gemstones of Montana, sapphires hold a special place in the Treasure State where they are readily found. Sapphires and rubies are both corundum, an aluminum oxide mineral typically found in crystalline form. The only difference between the two is the presence of chromium. If the corundum is red, it’s ruby. Otherwise, it’s always a sapphire.
One of the most desired types of gemstones, the most well-known sapphire hue is deep blue, but these gemstones are found in pink, green, violet, orange, purple and even brown. When they’re not blue, they’re referred to as fancy sapphires. These colors are because of the varying degrees of chromium, titanium oxide and iron within the stones. Sapphires also possess a trait called asterism where needle-like inclusions create the appearance of a six or twelve-patterned star. Beyond this unique characteristic appreciated by faceters, sapphires have a Mohs Amy Grisak; Getty Images/Science Photo Library value of nine, just below a diamond, making them extremely durable and an excellent choice for jewelry.

Tiger’s Eye
This distinct gem has a long history of fending off the “evil eye,” with its resemblance to a cat’s eye. In gemology, this trait is called chatoyancy, a French term meaning “shining like a cat’s eye.” When there are crocidolite (blue asbestos) fibers within cabochon-cut gemstones running parallel to each other, the rounded surface allows the light to reflect in a way that gives the tiger’s eye its signature look. Originally, scientists thought this phenomenon occurred when the crocidolite within the stone was changed by iron oxide and replaced with silica. But even though the coloration comes from this process, some researchers believe it’s actually crocidolite inclusions within columns of quartz within the stone that form the distinct paralleling nature.
Regardless of how it formed, tiger’s eye is a favorite gem for tumbling and with a Mohs value of seven, it’s a versatile stone for a multitude of uses. While it’s a ubiquitous stone these days, in the 1870s a single carat of tiger’s eye was worth an ounce of gold.

Unakite
Unakite is a terrific example of when a gemstone is a true rock as this beautiful pink and green specimen is a composite of metamorphic rocks including orthoclase, epidote and milky quartz. It’s formed during hydrothermal metamorphosis when the epidote replaces the silicate minerals, primarily plagioclase, within the granite. The epidote is green within unakite, while the pink orthoclase feldspar and quartz create the colorful speckling.
First found in the Unakas Mountains of Western North Carolina and Eastern Tennessee, it’s sometimes found in the rivers of the region, along with the beaches of Lake Superior where glaciers deposited the metamorphic rocks. With a Mohs rating of six to seven, unakite is among the types of gemstones that tumble well. It has been used to make small sculptures or is cut for jewelry. As eye-catching as it is, unakite is also valuable in construction on many levels, including being used as trim along the front steps of the south entrance of the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. It is also sometimes used less visibly as crushed stone in highway construction.
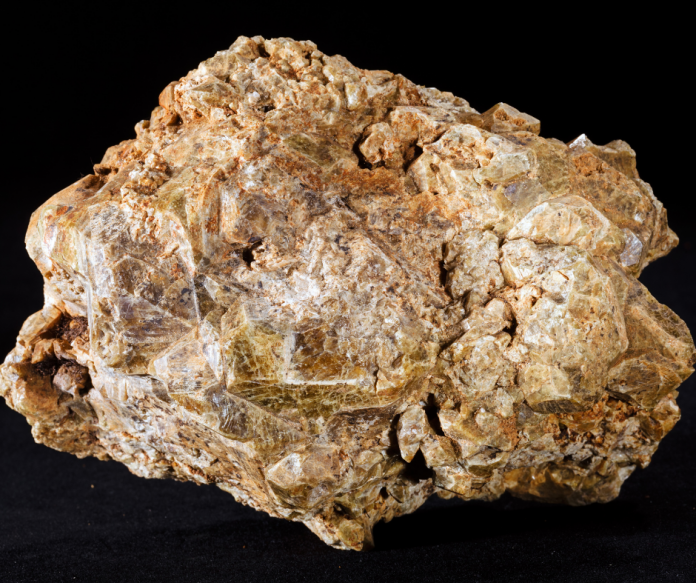
Vesuvianite
Sometimes called idocrase, vesuvianite was originally found along Mount Vesuvius in Italy, which buried the nearby inhabitants of the city of Vesuvius on August 24 in 79 AD, ironically during the festival of Vulcanalia, the god of fire. In the world of gem cutting, vesuvianite often refers to the rough stone, while the faceted gems are called idocrase.
Regardless of the name, this is a calcium-aluminum-silicate mineral that forms in a tetragonal structure. Its most popular colorations range from yellowish green to brownish or olive green, although there is a blue version called cyprine that derives its color from trace amounts of copper. With a Mohs value of six, vesuvianite isn’t a very hard stone and is often used for larger jewelry and sculptures. In its green coloration, it’s sometimes mistaken for other types of gemstones like peridot, although vesuvianite is far rarer.

White Topaz
While topaz is found in practically the entire color range, the white topaz is the clear version and boasts a similar appearance to a diamond. Outside of cost, there are distinct differences between the two types of gemstones. Topazes and diamonds are closely alike in clarity and color, but brilliance is where diamonds shine. Hardness is another determining factor. Diamonds reign supreme rating at Mohs 10, while topazes register as a Mohs eight, considerably less durable with a greater risk of scratching.
Topaz is created when water and magma react during the metamorphic process creating pegmatite featuring natural topaz that is typically initially clear. While the wide variety of colors is because of impurities, such as chromium replacing the aluminum within the stone, white topaz is the gem in its purest form. Specific hues are also created with heat, irradiation or the application of metal oxides to enhance colors. Topaz also exhibits pleochroism where the gem exhibits different colors depending on its angle, although the white topaz tends to remain consistent in its coloration.
Xenotime
On occasion, there are types of gemstones cut from this rare earth mineral, often found in yellowish-orange to reddish-brown hues, although high enough quality stones to facet are rare.
Like topaz, xenotime is found in pegmatite formations, as well as igneous rock and gneiss. Uranium and thorium are often found within this stone, creating natural radioactivity, although it is more commonly seen as a source for the transition metal yttrium, which is used as an alloy in the production of camera lenses and lasers. Its name is derived from the Greek terms for “vain” and “honor” in an early scientist’s snarky rebuke of another. Initially, Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius believed he discovered a new element within the xenotime. This turned out to be the already known yttrium, which prompted mineralogist François Sulpice Beudant to throw down a bit of shade on the claim.
Yellow Kunzite
True gemologists might shudder at the inclusion of yellow kunzite in this types of gemstones list, but it’s an example of when marketing can be misguided. As a rule, kunzite is a pink to light purple variety of spodumene, a lithium-rich mineral found, once again, in pegmatite formations. Manganese gives kunzite those attractive colors. When the gem is yellow, it’s typically just called yellow spodumene. The name change might be a matter of one word sounding more appealing than the other, but it is still misleading as kunzite implies a specific hue. With a Mohs value of six and a half to seven, it is not a very durable gemstone, but it’s possible to find specimens of 20 carats or more. Spodumene, in general, is an important source of lithium, which is critical for car batteries, phones and medicine. It is mined in Afghanistan, Pakistan, California, North Carolina and South Dakota.

Zircon
Not to be confused with the synthetic cubic zirconia, zircon earned its place as a popular gemstone 2000 years ago. Found in sand and as part of many of the rocks throughout the world, zircon is one of the oldest minerals on earth. Because of its uranium content, scientists in Australia dated it back 4.4 million years. Not all zircons are radioactive, but those that are can be heat-treated to stabilize the integrity of the stone by slowing the degradation of the crystalline structure. In their natural form, zircons are found in colors ranging from clear to yellow, green, purple, brown and grays, which are typically caused because of radiation or impurities. Blue zircons, which have been popular since Victorian times, are created through heat treatments.
This story about types of gemstones by letter appeared in Rock & Gem magazine. Click here to subscribe. Story by Amy Grisak.