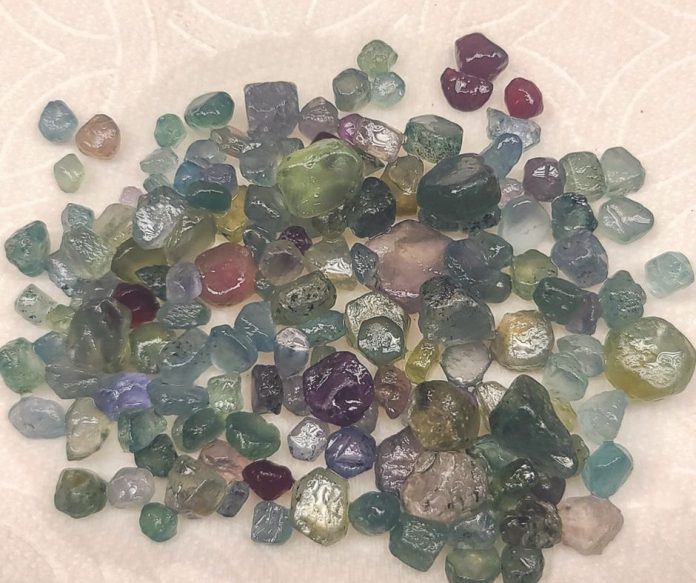
Montana sapphires today provide the inspiration and value that leads a whole new generation of folks to search for their own gems.
In over a century of searching, riches are still found in the “Treasure State” of Montana. Initially earning this moniker for the gold, silver and copper finds, sapphires have solidly earned their place among the bounty of the State.
During the Montana gold rush in Southwestern Montana in the early 1860s, sapphires appeared as colorful distractions in the miners’ pans and sluice boxes. The colorful bits of sand and gravel were of little value. While gold was one of the main forces, followed by silver and copper, behind the creation of Montana as a territory and a state, if the miners knew what they had at the time, they wouldn’t have been as quick to toss them aside.

“They were after the gold,” says Cass Thompson, owner and operator of the Spokane Bar Sapphire Mine, roughly 30 miles northeast of Helena. Thompson’s family has mined this area for sapphires over the past 60 years.
How Montana Sapphires Were Created
Created as igneous rocks slowly cooled, sapphires are made of the mineral corundum, chemically known as aluminum oxide. With a Mohs rating of nine, sapphires are the hardest natural substances following the diamond.
Reaching the level of the sapphire-laden material can be a challenge. Bound in a conglomerate of feldspar and bentonite clay, sapphires tend to settle well below layers of topsoil, overburden, and evidence of volcanic activity in the gravel bars. In some parts of the Eldorado Bar along the upper Missouri River deposit, there are layers 100 feet below the surface making it more difficult to reach. But because of the sapphires’ high specific gravity of four (although much less than gold’s 19.3) these areas were often intermingled with placer deposits, which is why they were intertwined with the search for gold.
The Brilliance of Chemistry
“We have quite a variety of sapphires in Montana, but the mainstay is the Yogo,” said Glenn McCaffery, longtime gem enthusiast in Great Falls, Montana, and registered jeweler with the American Gem Society.

“The Yogo is untreated and of exceptional quality. There are very few flaws,” he explained. While mining for gold in 1895 along Yogo Creek in the Little Belt Mountains east of Great Falls, prospector Jake Hoover collected the brilliant blue stones instead of discarding them, and sent them to Tiffany & Co. in New York City for an assessment. It turns out these excellent quality gemstones earned Hoover and his partners $3750, over $3000 more than what they’d made finding gold.
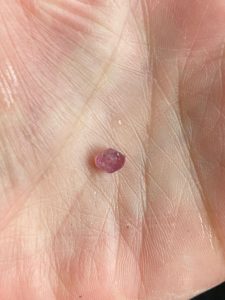
While the beautiful “cornflower blue” of the Yogo is highly desirable, natural sapphire colors range from lighter blues, lavenders, pinks, greens, oranges and yellows. Combinations of titanium, iron, small amounts of chromium, and nickel result in this wide array of hues. The signature coloration of the Yogo is a result of titanium and iron, with the more iron involved, the deeper the blue. Rubies, which are also corundum and sometimes found in these areas, are brilliant red because of the presence of a higher concentration of chromium.
“In the Missouri River Deposit where we mine, we get the full spectrum of colors, but the most prominent is the blue/green,” said Thompson. He also notes they find a wide range of sizes.
More Valuable than Gold
“We’ve seen some really nice gem-quality sapphires up to a 26 facet grade,” said Thompson.

Photo by Cass Thompson.
When searching for sapphires, sharp eyes are needed to pick out the tiny gems that are mere millimeters across, but larger stones closer to 10 carats are not uncommon. “The largest was found by my grandfather. He found a 50-carat stone. I’m still in the high 20s,” he said. To put it in perspective, Thompson said a 50-carat sapphire is roughly one and a half inches long and as big around as a man’s thumb.
The popularity and price of sapphires, especially since they are September’s birthstone, today would make early prospectors swoon. Thompson said some of the stones found on their place were valued between $1000 to $10,000 per carat. As an example, Thompson said a 24-carat sapphire cut to an 8 to 9-carat finish is easily worth $10,000 or more. “The value (of sapphires) is definitely more than gold,” he said.
Where Montana Sapphires are Found

Besides Yogo Gulch between Great Falls and Lewistown, which is no longer open to the public, there are many sapphire-rich areas throughout Central and Southwestern Montana, all of which coordinate with historic gold speculation. The gravel bars running along the upper Missouri River between Canyon Ferry Reservoir and into Hauser Lake, including the Eldorado and Spokane Bars, are some of the earliest finds and are still rich in sapphires. But after the construction of the dam in the early 1900s to create Hauser Lake, several of the gravel bars were submerged deep below the surface. It’s interesting to consider what sapphires are strewn along these now underwater former gold stakes when prospectors tossed the pretty stones aside.
More to the southwest, the Dry Cottonwood Creek (discovered in 1889) near Deer Lodge, as well as Rock Creek closer to Philipsburg, which was also found in the late 1800s, became popular sapphire mining areas. While the high-quality gems of Yogo Creek earned impressive amounts, many of the other sapphires initially found industrial uses, primarily in watchmaking, as well as being used in bombsights for torpedos and as the abrasive material on sanding wheels until the mid-1940s. After this time period, industrial operations shifted to synthetic sapphires to suit their needs. Since then, treasure hunters still gravitate toward several of these historic mining locations.
Want to Try your Hand at Finding your Own Montana Sapphires?Touch base with these knowledgeable operations for your treasure hunt. Not far from the state capital of Helena, the Spokane Bar Sapphire Mine offers several digging options.  Located in Philipsburg, Gem Mountain offers material at a downtown shop or at the mine roughly 22 miles out of town. Whether searching gravel on-site or having it shipped to your own, Montana Gems offers materials from Rock Creek and the Eldorado Bar areas. Also in Philipsburg, the Sapphire Gallery offers materials from the Rock Creek deposit in the aptly named Sapphire Mountains. |
Commercial Mining
Montana is the only state where sapphires are commercially mined, which includes providing opportunities for the public to try their hand picking through gravel to find treasure. Thompson said the basic premise of sapphire mining hasn’t changed very much over the past century. “Since we’ve been doing it, it’s pretty much the same. The equipment just gets bigger,” he says. Front-end loaders and excavators are the front line in removing the materials from the mining location before further processing.
For operations that sell gravel for individuals and families, it’s not a matter of simply dumping dirt and gravel into a bucket. Once extracted, the material goes through a trommel, a rotating drum that sorts out the larger rocks, followed by multiple screening and washing processes to refine the material to a manageable size. In the end, what’s left is a bucket of seemingly innocuous gravel and clay that is rich with Montana sapphires, along with possibly topaz, hematite, garnets, fossils and even gold.
Digging Montana Sapphires

Is it legal to collect rocks, including Montana sapphires? Many commercial mines are open to the public throughout the state with the option of visiting the mining area and searching through the gravel outdoors in a beautiful setting. Some allow visitors to gather material to gain a better understanding of the process. Other places have storefront facilities where there is typically an option to purchase a bucket to sort through at the shop or buy materials to take home. Most mines can even ship bags of gravel.
The actual sorting process is fairly simple. Customers are given a shaker box, which is a screened, roughly three-inch tall container that allows the water to flow through the materials. It is filled about halfway with gravel, then washed in a large tub or trough.

Washing is somewhat of a zen moment. The rhythmic motion of gently working the shaker box in the water — submerge, tilt, flatten, turn, repeat — is surprisingly relaxing. With these movements in the water, the gravel rises, and because the sapphires are heavier, they sink below the layer. Washing also filters out the fine clay to make the gems more visible. After a few passes, it’s time to flip the box on the table so the sapphires are closer to the top.
It doesn’t take long to train your eye to see the pastel colors and different shapes, which are sometimes more rounded or potentially crystalline depending on the mine location. Tweezers are the tool of choice to pluck them from the gravel. Because there can be several different minerals among the sapphire material, if there is any question, save the stones and ask someone at the mine. With generations of experience, they’re happy to explain your find and answer questions.
As with many outdoor activities in Montana, operating seasons are dictated by the weather. Some of the indoor shops offer gravel washing throughout the year, but for those who want to hunt at the mine sites, it’s best to wait until the weather moderates. Thompson said that they’ll often continue mining into December, which can be a brutal month. If Mother Nature cooperates, they welcome visitors in March or April.
Treasure Hunting
Steeped in a long tradition of treasure hunting, Montana sapphires are a unique find in this extraordinarily beautiful landscape.
Picking through pay dirt, it’s easy to understand the allure of gold, and later these colorful gems, and why this quest never fails to spark the heart and imagination of those who appreciate the challenge.
This story about Montana sapphires previously appeared in Rock & Gem magazine. Click here to subscribe! Story by Amy Grisak.